The Behavior Wizard is a method for matching target behaviors with solutions for achieving those behaviors. It is a systematic way of thinking about behavior change. The Behavior Wizard expands the Behavior Grid and the Behavior Model by combining our best work into one easy-to-use solution.
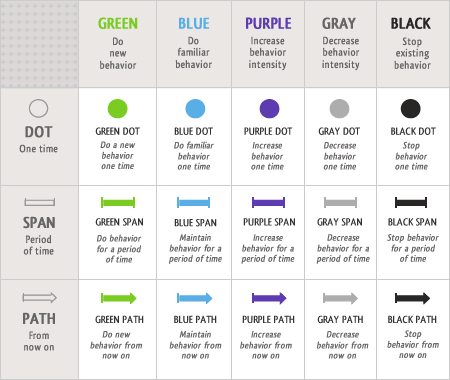
Fogg Behavior Grid – 15 Ways Behavior Can Change
The Fogg Behavior Grid outlines 15 types of behavior as defined by BJ Fogg. The grid describes the ways behavior can change. Its purpose is to help people think more clearly about behavior change.
Each of the 15 behaviors types uses different psychology strategies and persuasive techniques. For example, the methods for persuading people to buy a book online (BlueDot Behavior) are different than getting people to quit smoking forever (BlackPath Behavior).
With this framework, people can refer to specific behaviors like a “PurpleSpan Behavior” or a “GrayPath Behavior.” For example one might say, “The Google Power meter focuses on a GrayPath behavior.” These new terms give precision.
But this innovation goes beyond identifying the 15 types of behavior change and giving them clear names. The model also propose that each behavior type has its own psychology. And this has practical value: Once you know how to achieve a GrayPath Behavior, you can use a similar strategy to achieve other GrayPath Behaviors (for example, getting people to watch less TV). In this way, the Behavior Grid can help designers and researchers work more effectively.
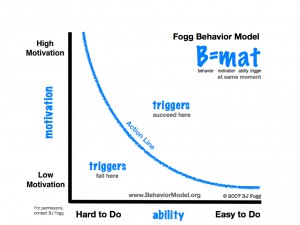
Fogg Behavior Model – What Causes Behavior Change?
The Fogg Behavior Model shows that three elements must converge at the same moment for a behavior to occur: Motivation, Ability, and Trigger. When a behavior does not occur, at least one of those three elements is missing.
Using the Fogg Behavior Model (FBM) as a guide, designers can identify what stops users from performing behaviors that designers seek. For example, if people are not performing a target behavior, such as rating hotels on a travel web site, the FBM helps designers see what psychological element is lacking.
The FBM also helps academics understand behavior change better. What was once a fuzzy mass of psychological theories now becomes organized and specific – and practical –when viewed through this model.
The Behavior Wizard & Resource Guides
To make this approach to behavior change clearer and more useful, we created the Behavior Wizard and Resource Guides for each of the 15 types of behavior change. Each guide gave more examples, explained relevant theories, and highlighted real-world techniques for achieving the specific behavior type.
We felt that in the past, most designers and researchers guessed at solutions for changing behavior. And frankly we saw that most attempts failed. Rather than guessing at solutions, people who used our Resource Guides had clear guidance. The Behavior Wizard generated these Resource Guides, drawing on the ever-improving content our team created (it was like wikipedia for specific types of behavior change).
UPDATE
The Behavior Guides were created in 2010 and we are no longer updating or selling them.
There is still lots of useful information in these guides. If you’re interested in obtaining a specific guide, please email us (captology@stanford.edu) and let us know in which guide you’re interested and why. We may be able to share a copy with you.
Behavior Wizard Project Team
The following people have contributed their time and energy to this project.
BJ Fogg, Project Director
Jason Hreha, Project Lead
Robin Krieglstein, Web Developer
Kara Chanasyk, UX Designer
Gaj Krishna, Research Specialist
Gaju Bhat
Shuqiao Song
Visit www.behaviorwizard.org to learn more.